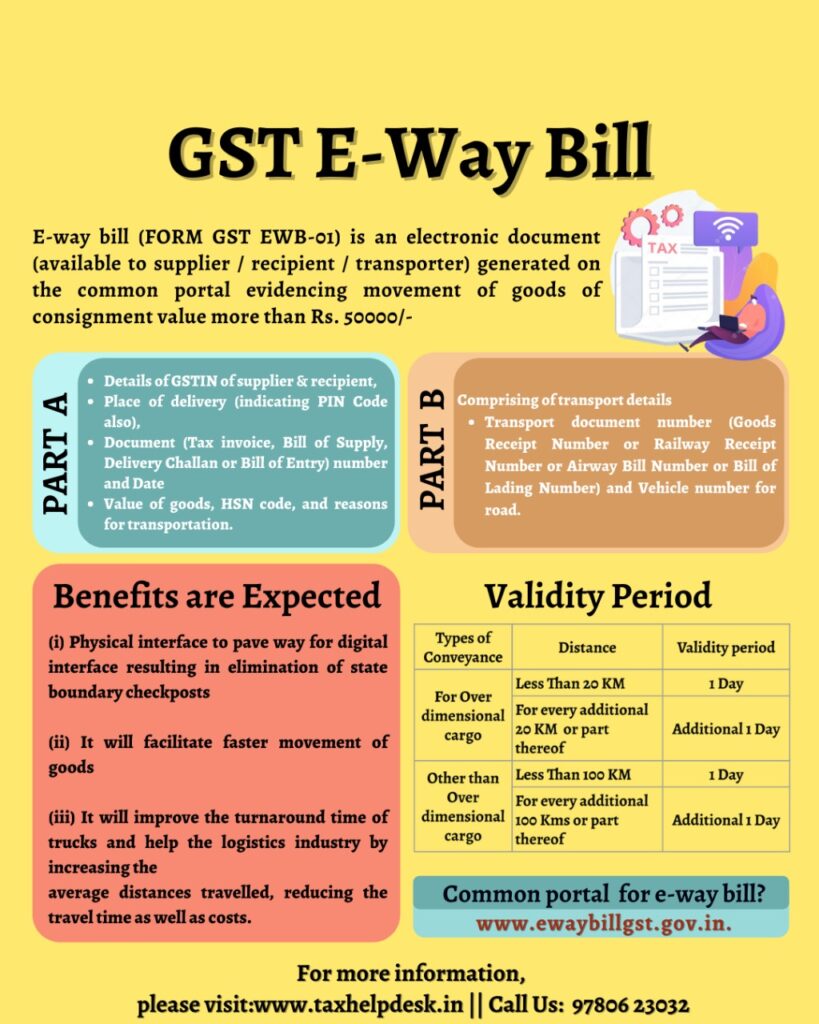
GST E-way bill is an electronic document generate on the GST portal evidencing the movement of goods.
E-way bill system has two Components – Part A and Part B
– Part A comprises of details of GSTIN of the recipient, place of delivery (PIN Code), invoice or challan number and date, the value of goods. In addition to this, it also contains HSN code, transport document number (Goods Receipt Number or Railway Receipt Number or Airway Bill Number or Bill of Lading Number) and reasons for transportation.
– Part B comprising of transporter details (Vehicle number)
Note:
Through the amendment in December 2020, now the kms for “other than over dimensional cargo” is 200 kms from 100 kms.
When Is The GST E-Way Bill To Be Issued?
Every registered person who causes movement of goods of consignment value more than Rs. 50000/-is required to furnish information in Part A of the e-way bill. On the other hand, Part B containing transport details helps in the generation of e-way bills.
Movement of goods or consignment can be
– In relation to a supply
– For reasons other than supply (eg: Return of goods)
– Due to inward ‘supply’ from an unregistered person
Also Read: Relevance of Supply under GST
Further, supply can be made for
– Consideration (payment) in the course of business
– Consideration (payment) which may not be in the course of business
– Without consideration
Exceptions to the above Rule
For certain specified Goods, the GST e-way bill system needs to be generate mandatorily. Even if the value of the consignment of Goods is less than Rs. 50,000:
– The goods are sent by a principal located in one State to a job worker located in any other State, the e-way bill shall be generated by the principal irrespective of the value of the consignment.
– Handicraft goods are transport from one State to another. In addition, who exempt from the reHandicraft goods are transported from one State to another by a person who has been exempted from the requirement of obtaining registration.
Who Is Required To Generate GST e-way bill?
E-way bill is to be generated by the consignor or consignee himself, if the transportation is being done in own/hired conveyance or by railways by air or by vessel. If the goods are handed over to a transporter for transportation by road, eWay Bill is to be generated by the transporter. Where neither the consignor nor consignee generates the eWay Bill and the value of goods is more than Rs.50,000/- it shall be the responsibility of the transporter to generate it.
Also Read: Can you claim GST ITC on Travel?
Cases Where GST e-way bill Is Not Required To Be Generated?
In the following cases it is not necessary to generate GST e-way bill:
- The mode of transport is non-motor vehicle
- Goods transported from Customs port, airport, air cargo complex or land customs station. In addition in order to Inland Container Depot (ICD) or Container Freight Station (CFS) for clearance by Customs.
- Goods transported under Customs supervision or under customs seal
- If goods are transported under Customs Bond from ICD to Customs port or from one custom station to another.
- Transit cargo transported to or from Nepal or Bhutan
- Movement of goods caused by defence formation under Ministry of defence as a consignor or consignee
- Empty Cargo containers
- Consignor transporting goods to or from between place of business and a weighbridge is for weighment at a distance of 20 kms, accompanied by a Delivery challan.
- Goods being transported by rail where the Consignor of goods is the Central Government, State Governments or a local authority.
Note:
Part B of eWay Bill is not required to be filled where the distance between the consigner or consignee and the transporter is less than 50 Kms and transport is within the same state.
How Is GST e-way bill Generated?
An eWay Bill contains two parts- Part A to be furnished by the person who is causing movement of goods of consignment value exceeding Rs.50,000/- and Part B (Transport Details) to be furnished by the person who is transporting the goods. Where the goods are transported by a registered person whether as consignor or recipient, the said person shall have to generate the e-way bill by furnishing information in Part B on the GST common portal.
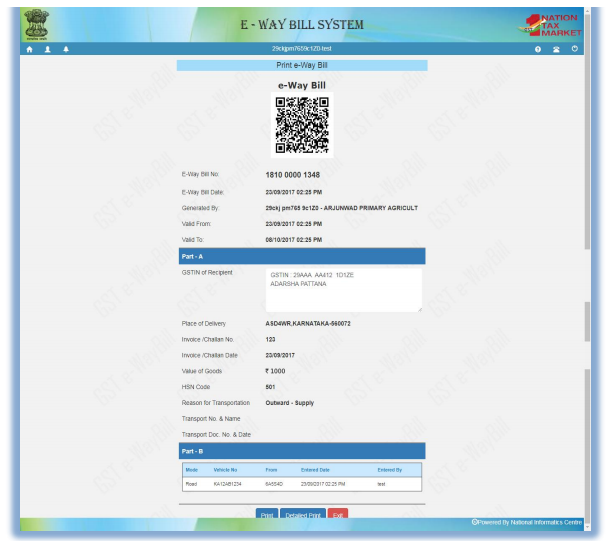
Where the eWay Bill is not generated by registered person and the goods are handed over to the transporter for transportation by road, the registered person shall furnish the information relating to the transporter in Part B of FORM GST EWB-01 on the common portal and the e-way bill shall be generated by the transporter on the said portal on the basis of the information furnished by the registered person in Part A of FORM GST EWB-01.

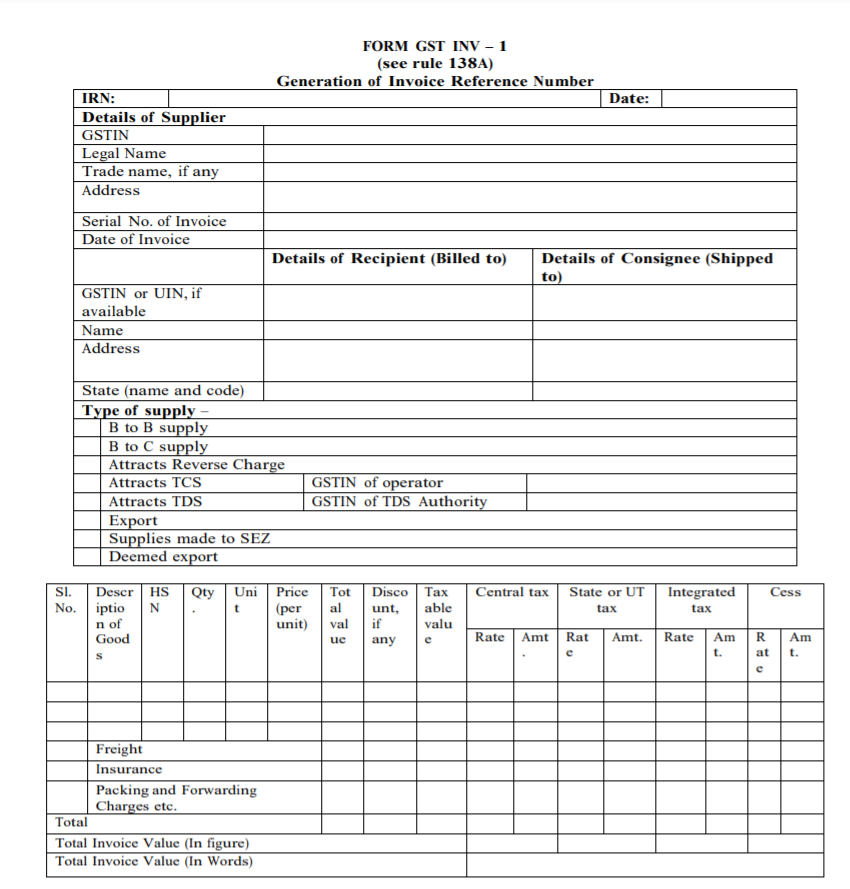
A registered person may obtain an Invoice Reference Number from the common portal by uploading, on the said portal, a tax invoice issued by him in FORM GST INV-1 and produce the same for verification by the proper officer in lieu of the tax invoice and such number shall be valid for a period of thirty days from the date of uploading.
In the above case, the registered person will not have to upload the information in Part A of FORM GST EWB-01 for generation of e-way bill and the same shall be auto populated by the common portal on the basis of the information furnished in FORM GST INV-1.
Documents Required For GST e-way bill Generation?
The e-way bill system require the following documents to generate the bill:
- Invoice/ Bill of Supply/ Challan relate with the consignment of goods
- Transport by road – Transporter ID or Vehicle number
- And, if transport by rail, air, or ship – Transporter ID, Transport document number, and date on the document
Validity of GST e-way bill
An eWay Bill is valid for duration as listed below, which is based on the distance travelled by the goods. Validity is calculated from the date and time of generation of eWay Bill:
| Type of conveyance | Distance | Validity of EWay BIll |
|---|---|---|
| For Over dimensional cargo | Less Than 20 Kms | 1 day |
| For Over dimensional cargo | For every additional 20 Kms or part thereof | Additional 1 day |
| Other than Over dimensional cargo | Less Than 200 Kms | 1 day |
| Other than Over dimensional cargo | For every additional 200 Kms or part thereof | Additional 1 day |
Cancellation of GST e-way bill
Where an eWay Bill has been generated under this rule, but goods are either not transported or are not transported as per the details furnished in the eWay Bill, then it may be cancelled electronically on the common portal, either directly or through a Facilitation Centre notified by the Commissioner, within 24 hours of generation of the Bill. However, an eWay Bill cannot be cancelled if it has been verified in transit in accordance with the provisions of rule 138B of the CGST Rules, 2017 .
Consequences of non-conformance to GST e-way bill rules
If eWay Bill, wherever required, are not issued in accordance with the provisions contained in Rule 138 of the CGST Rules, 2017, the same will be considered as contravention of rules. As per Section 122 of the CGST Act, 2017, a taxable person who transports any taxable goods without the cover of specified documents (eWay Bill is one of the specified documents) shall be liable to a penalty of Rs.10,000/- or tax sought to be evaded (wherever applicable) whichever is greater.



Informative