As per the Income Tax laws of India, anything received by person in monetary terms is treated as an income of that person. The income of source could be salary, income from house rent, gift from relatives, income from house rent and many more. Furthermore, if this income exceeds the exemption limit, then the person will have to pay taxes and file his Income Tax Return. In this blog, we will tell you in detail about the ways to save tax apart from claiming deductions under Section 80C.
Details of Income from sources and their limit for the ways to save tax
- Salary
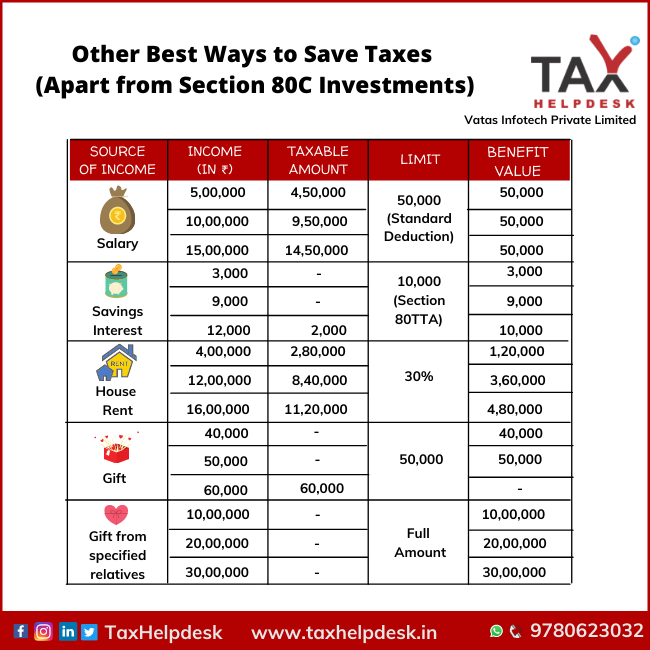
Every salaried individual can save taxes on income of flat Rs. 50,000 by way of Standard Deduction on his taxable income. This amount of standard deduction is not dependent on any of the expenses of the individual. Earlier the limit of standard deduction was Rs. 40,000 but from Financial Year 2019-2020, it has been increased to Rs. 50,000/-. Also, now, the standard deduction is available under the old tax regime as well as new tax regime.
Particulars Till FY 2018-2019 FY 2019-2020 FY 2020-2021 FY 2021-2022 FY 2022-2023 FY 2023-2024 Standard Deduction N/A Rs. 40,000 Rs. 50,000 Rs. 50,000
(available only under the Old Tax Regime)
Rs. 50,000
(available only under the Old Tax Regime)
Rs. 50,000
(available only under both the Tax Regimes)
- Income from interest on savings account
Interest on the savings account is treated as “income from other sources” and is added in the total income of the person. However, as per Section 80TTA, an individual below the age of 60 years can save taxes of upto Rs. 10,000 on this income earned from interest on the savings account. On the other hand, individuals above 60 years can save taxes of upto Rs. 50,000 through income from interest on savings account.
Particulars Income Exempted (Below 60 years) Income Exempted (Above 60 years) Income through interest on savings account Rs.10,000 Rs. 50,000 Also Read: Deductions on interest earned by senior citizens under Section 80TTB
- Income from House Rent
As per Income Tax Act, rental income of a property is taxed under Section 24A in the hands of the owner, under the head ‘income from house property’. However, the rent earned by letting out vacant land is not taxed under this category, but is taxed under ‘income from other sources’. If an individual receives income from house rent, then he is allowed to deduct the municipal taxes payable for the property. As the rent is taxable on accrual basis, the law allows individual to claim deduction for the rent which he has not been able to realise, subject to the fulfilment of certain conditions. After deducting the above two items, what is left is the annual value, on which standard deduction of 30% of the annual value can be claimed and tax can be saved.
Particulars Amount Gross Annual Value ***** Less: Municipal Taxes (*****) Net Annual Value (*****) Less: Deduction under Section 24 Standard Deduction @30% (*****) Interest on borrowed capital (*****) Income from House Property ***** - Gifts
As per the Income Tax laws, gift (cash or in kind) is also treated as “income from other sources” and is taxable if the value of the gifts exceeds Rs. 50,000/-. If the money given as a gift is above Rs. 50,000, then the whole amount becomes taxable and not the amount beyond Rs. 50,000/-
Gifts
Type of Gift Recipient’s Relationship to Donor Tax Implications Money Any person Taxable as income for the recipient if the aggregate value exceeds Rs. 50,000 in a financial year. Immovable Property Any person Taxable as income for the recipient based on the stamp duty value of the property if the aggregate value exceeds Rs. 50,000 in a financial year. Movable Property Any person Taxable as income for the recipient if the aggregate fair market value exceeds Rs. 50,000 in a financial year. Gifts received on occasions (e.g., wedding, inheritance, etc.) Any person related to the recipient Exempt from tax. There are no tax implications for gifts received from specified relatives on special occasions. - Gifts from specified relatives
As stated in the above point, money in the form of gift is treated as “income from other sources” and is taxable under the Income Tax Act. However, if the gift has been received from the specified relatives, then the whole amount of gift is exempted from Income Tax. So it is the ways to save tax.
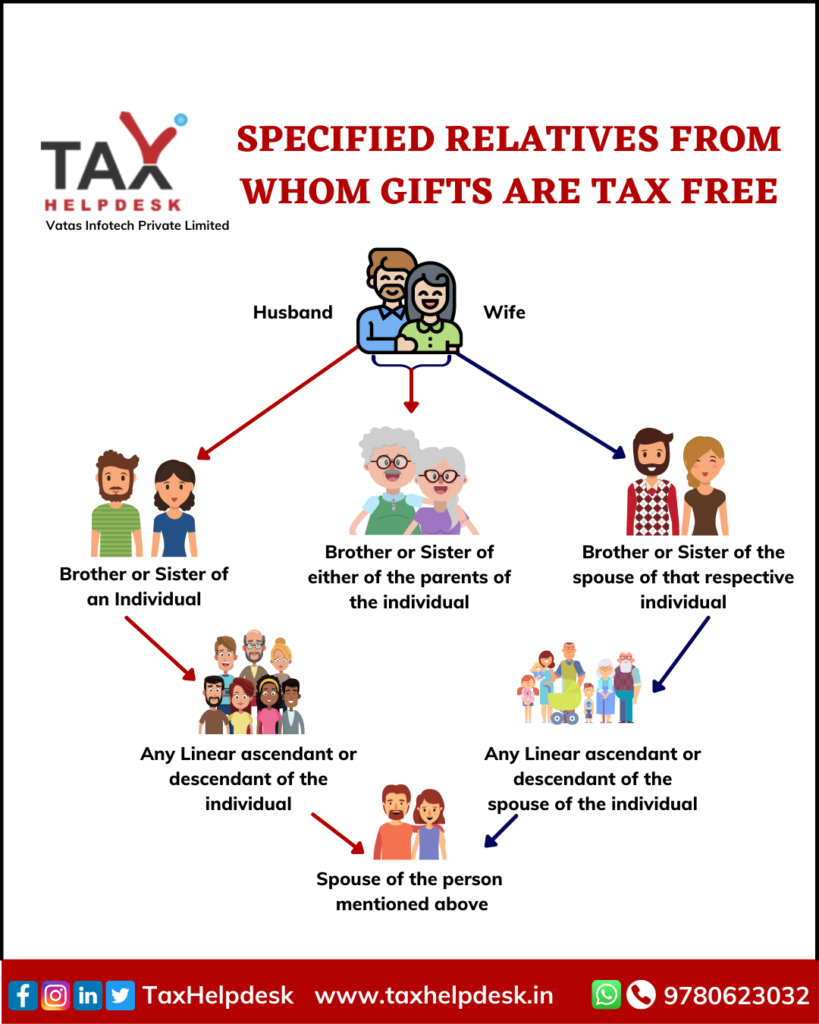
These specified relatives are spouse, father, mother, brother and sister. They also include any lineal ascendant or descendant of the individual or his spouse as well as brother/sister of the spouse.
Also Read: Restriction On Cash Transactions Under The Income Tax Act
However, note that even though the gift itself is exempted in the hands of the recipient, the income generated from the gift may be taxable under the clubbing of income provisions of the Income Tax Act.
| Type of Income | Clubbing Provisions |
|---|---|
| Income from Assets transferred to Spouse without adequate consideration | If an individual transfers income-generating assets to their spouse without adequate consideration, the income generated from those assets will be clubbed with the income of the transferor. |
| Income from Assets transferred to Son’s Wife without adequate consideration | If an individual transfers income-generating assets to their son’s wife without adequate consideration, the income generated from those assets will be clubbed with the income of the transferor. |
| Income from Assets transferred to Any Other Person without adequate consideration | If an individual transfers income-generating assets to any other person without adequate consideration, and the main purpose of the transfer is to avoid tax, the income generated from those assets will be clubbed with the income of the transferor. |
| Income of Minor Child | Any income earned by a minor child (below 18 years of age) is clubbed with the income of the parent who has the higher income, except in certain specified cases such as income from manual work or specialized skills. |
| Income from Spouse’s Remuneration, Business, or Profession | If income is earned by a spouse directly or indirectly from the remuneration, business, or profession of the other spouse, it is clubbed with the income of the spouse who earns it. |
| Income from Assets Transferred to a Revocable Transferor | If an individual transfers assets to a revocable transferor, and the income from those assets is still attributable to the transferor, it will be clubbed with the income of the transferor. |
If you want to know more about cash payments restrictions or take TaxHelpdesk’s experts consultation, then drop a message below in the comment box or DM us on Whatsapp, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn and Twitter. For more updates on tax, financial and legal matters, join our group on WhatsApp and Telegram!
Disclaimer: The views are personal of the author and TaxHelpdesk shall not be held liable for any matter whatsoever!


Pingback: Best ways to save taxes (other than Section 80C...