Many people own capital assets but are not aware of the taxability. In this blog, we will explain in detail about the taxability of capital asset in India.
What are Capital Assets?
Section 2(14) of the Income Tax Act specially defines capital assets. As per this definition, it means
– Property of any kind held by an assessee
– Securities recognized by SEBI, held by a Foreign Institutional Investor
– ULIPs to which exemption under Section 10(10D) does not apply
– Urban agricultural land
Also Read: How To Adjust Profit/Losses From Transfer Of Shares
Test to determine Capital Assets
In order to determine whether something is a capital asset or not, it should not be any of the following:
– Any stock-in-trade, consumables or raw material held for the purpose of business of profession
– Any personal effects such as movable property – wearing apparel and furniture held for personal use by the assessee or his family members
– Rural agricultural land
– 6½% gold bonds gold bonds (1977) or 7% gold bonds (1980) or national defence gold bonds (1980) issued by the central government
– Special bearer bonds (1991)
– Gold deposit bond issued under the gold deposit scheme (1999) or deposit certificates issued under the Gold Monetisation Scheme, 2015
Also Read: Difference between Sensex and Nifty
Types of a Capital Asset
A Capital Asset can be of two types:
– Long Term
– Short Term
Long Term Capital Asset: An asset whose holding period is more than 12/24 months is a long-term capital asset. Further, this duration depends upon the type of asset.
Short Term Capital Asset: On the other hand, an asset whose holding period is less than 12/24 months is a short-term capital asset. And, just like long term capital assets, short term capital assets also depend upon the type of asset.
Also Read: Tax Benefits On Home Loan: Know More At TaxHelpdesk
Duration of a Capital Asset
The duration of a capital asset depends on the type of asset, which is as follows:
| Capital Asset | Long Term Duration | Short Term Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Immovable property (eg: Land) | More than 24 months | Less than 24 months |
| Movable property (eg: Jewellery) | More than 24 months | Less than 24 months |
| Shares recognised by SEBI | More than 12 months | Less than 12 months |
| Unlisted Shares | More than 24 months | Less than 24 months |
| Equity Oriented Mutual Funds | More than 12 months | Less than 12 months |
| Debt Oriented Mutual Funds | More than 24 months | Less than 24 months |
| Other Assets | More than 24 months | Less than 24 months |
Union Budget 2024
– There is a decrease in holding period of certain capital assets wrt long-term capital gains from 36 months to 24 months.
Examples of Capital Assets:
Shares
If the assessee holds the shares for trading purposes, then it is not treated as a capital asset. However, if he holds these shares for non-trading purposes, then it is treated as a capital asset. Further, the stocks are divided into two parts:
– Listed Shares
– Unlisted Shares
Also Read: How To Treat Capital Gain From Transfer Of Shares
The taxability on the sale of shares depends upon type and duration are as follows:

Mutual Funds
Mutual funds being movable property are capital assets. The mutual funds are of 2 types:
– Equity Oriented Mutual Funds (investment in equities is more than 65% of the total portfolio)
– Debt Oriented Mutual Funds (investment in equities is less than 65% of the total portfolio)
Also Read: Know Types & Taxability Of Mutual Funds SIP
The taxability of these types of mutual funds depends upon the duration of holding. The following image explains the taxability of Mutual Funds:

Note:
Through the Union Budget, 2023 no indexation benefit will be available while calculating long-term capital gains on Specified Mutual Fund (i.e a mutual fund which invests less than 35% of its proceeds in the equity shares of domestic companies). Debt mutual funds will now be taxed as per the applicable slab rates.
Land & Building
Land & building is a property which is also a capital asset and the profit on sale of such land and building is a capital gain. And, the taxability rates on the basis of duration are as follows:
Also Read: Know Tax Benefits Of Purchasing Property Through Home Loan

Cars
A car is a capital asset if it is used for business purposes. This is because it allows for depreciation. On the other hand, the car purchased for personal purposes is not considered to be a capital asset.
Jewellery
Jewellery like gold, silver, diamond, precious stones, etc is also capital assets. Consequently, any profit made on the sale of it is treated as a capital gain.
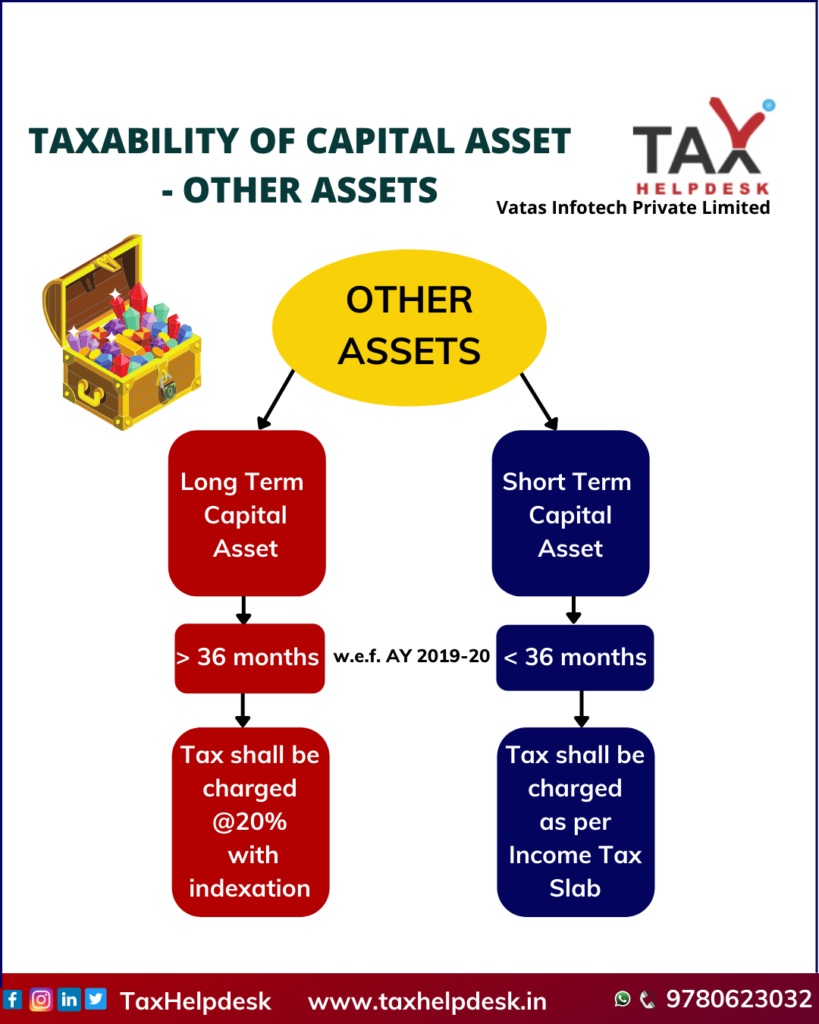
Some Other Examples Of Capital Assets:
Art and Collectibles
Till 31st March, 2007, art and collectibles was not considered to be a capital asset. However, from 1st April, 2007 the gain is no longer tax-free since the definition of capital asset has been amended to include paintings, sculptures, drawings, archaeological collections or any work of art.
Also Read: Ways to Save Taxes in 2022!
Business Assets
With respect to assets that are used for the purpose of business, tax payers are allowed to claim depreciation on the cost of acquisition of such assets. In addition, the depreciation, under the income tax laws, for such assets is allowed, on the basis of a concept called ‘block of assets’. The profit (Sale price – Written down value) on sale of such asset will be taxed as business income under the head “Profits or Gains from Business or Profession”. Therefore, it is considered as a capital asset and profit on sale of such asset is capital gain.
Cryptocurrency
The cryptocurrency is a property held by the assessee. Earlier, there was no provision for taxing of the virtual currencies. But through the budget of 2022, the cryptocurrencies shall be taxable at 30%.
Thereby, a new section namely Section 115BBH(1) was inserted in the Income Tax Act.
Furthermore, post April 1, 2022, both short term and long term virtual digital currency will be taxed at flat 30%. This is applicable even if the income from digital asset is treated under the head income from business or profession or income from other sources.
Conclusion
| Capital Asset | Long Term Duration | Long Term Taxability | Short Term Duration | Short Term Taxability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immovable property (eg: Land) | More than 24 months | 20% with Indexation | Less than 24 months | As per the Income Tax Slab |
| Movable property (eg: Jewellery) | More than 36 months | 20% with indexation | Less than 36 months | As per the Income Tax Slab |
| Shares recognised by SEBI | More than 12 months | 10% in excess of Rs. 1 lac | Less than 12 months | 15%, irrespective of the amount |
| Unlisted Shares | More than 24 months | 20% with indexation | Less than 24 months | As per the Income Tax Slab |
| Equity Oriented Mutual Funds | More than 12 months | 10% in excess of Rs. 1 lac | Less than 12 months | 15%, irrespective of the amount |
| Debt Oriented Mutual Funds | More than 36 months | 20% with indexation | Less than 36 months | As per the Income Tax Slab |
| Cryptocurrency | More than 36 months | 30% | Less than 36 months | 30% |
Have anymore questions wrt capital assets or would want to speak with one of the TaxHelpdesk’s experts, then please leave a message below in the comment box or DM us on Whatsapp, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn and Twitter. Join our Telegram group for more information on tax, financial, and legal matters!
Disclaimer: Viewpoints of the author his or her own, and TaxHelpdesk is not responsible for anything!



Pingback: Know About Systematic Investment Plan (SIP) | TaxHelpdesk
Pingback: Brief Analysis of Income Taxes & It’s Working In India | TaxHelpdesk