What is Cheque?
As per Section 6 of Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881 – A “cheque” is a bill of exchange drawn on a specified banker and not expressed to be payable otherwise than on demand and it includes the electronic image of a truncated cheque and a cheque in the electronic form.
It contains instruction in written given by the account holder to his bank for the payment of the money from his account. There is a statutory obligation of the part of the banker to make the payment if the following conditions are fulfilled:
- The cheque is properly drawn
- There is sufficient balance in the account
- There is no legal restraint o the bank’s duty to pay the amount.
What is Bouncing of Cheque?
Bouncing of cheque in simple terms is a situation where the cheque is not honoured due to several reasons. However, one of the most main reasons for the bouncing of cheque is the Non-Sufficient Balance (NSF) in the account of the person issuing the cheque. Bouncing of cheque can be illegal if the issuer fails to honour the cheque.
Reasons for Bouncing of Cheque
- Non-Sufficient Funds: When the issuer’s account has insufficient funds or has less balance , then the bank is not able to honour the cheque. In such a case, the bank imposes a nominal penalty on both the issuer and depositor. The remedy lies with the issuer is to either issue a new cheque or resolve the issue with the depositor of the cheque. If the issuer fails to do so, then the depositor has legal remedy against the issuer for dishonour of cheque.
- Date mentioned on the cheque: The date on the cheque is one of the most important part of the cheque. This is so because the date mentioned on the cheque defines the period of limitation for withdrawing the amount or raising legal action, if the situation persists. The common problems which can be related with date on the cheque mainly includes disfigured, scribbled or overwritten digits.
- Mismatch in signature: This is the part over which the bank draws its major attention. Since, there are chances of forgery, the bank pays utmost attention to the signature on the cheque issued. If the signature is mismatched or does not match with the bank records, then the bank will tag such a cheque as bounced. Another case in which the cheque gets bounced is when the issuer happens to sign on MICR Band present on the cheque. Therefore, the issuer should be cautious while putting his signature on the cheque.
- Difference in Amount Mentioned in Numbers & Words: As per the Negotiable Instruments Act, if there is a difference between the amount mentioned in numbers and words, then the amount written is to be considered. But the banker holds the right to dishonour the cheque, in case of any such discrepancy. Also, if there are some numbers written along with the words or there are words written along with the numbers, then also the banker holds the right to dishonour the cheque.
- Disfigured Cheque: If the cheque that has been drawn is not presented properly or is damaged or is disfigured, in which the entries are not clearly visible, then the banker holds the right to dishonour the cheque.
Procedure for remedy in case of Bouncing of Cheques as per Section 138 of Negotiable Instruments Act
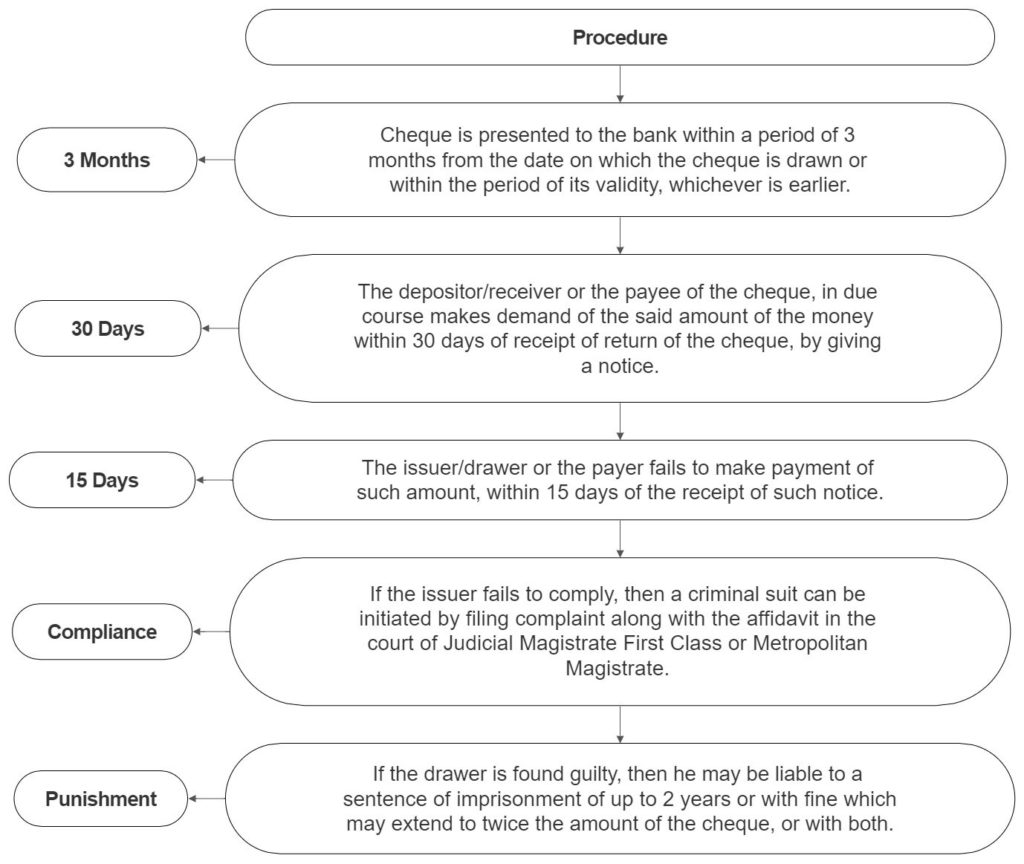
Please note that the above remedy is available only in the case of non-sufficient funds and bouncing of cheque in India is a criminal offence.
Contents Of The Cheque Bounce Notice
- Details of the issuer.
- Cheque was presented within the validity period.
- Return date of cheque with reasons.
- Demand notice to honour the cheque is served within 30 days time and 15 days time is given to honour the same.
FAQs
The circumstances in which a cheque bounce does not amount to an offence are numerous in number. Some of the instances are:
When the cheque is given as an advance.
- When the cheque is given as a security.
- The disparity in amount stated in words and figures.
- Alternations in cheques require attestation by the drawer.
- If the cheque is found mutilated.
- When a cheque is issued to a charitable trust as a gift or donation.
Yes, bouncing of cheque is a criminal offence in India with a punishment of imprisonment of up to 2 years or with fine which may extend to twice the amount of the cheque, or with both.
1) when the cheque is issued against a legal liability. 2) when the cheque in question is dishonoured because of insufficiency of funds, account closed, payment stopped by the drawer or similar other reasons. 3) Despite receiving of the demand notice the drawer of the cheque fails to make the payment within 15 days from the receipt of the notice.
If the Accused is ready to pay the cheque amount along with interest and cost as assessed by the Court by a specified date, then the Court is entitled to close the proceedings in exercise of its powers under Section 143 of the Negotiable Instrument Act read with Section 258 Code of Criminal Procedure.



















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.