Brief overview of Sole Proprietorship Firm
Sole proprietorship is a firm that owned and managed by the sole proprietor. In the eyes of law, there is no difference between the proprietor and the sole proprietorship and are treated as one.
List of Compliances involved in Sole Proprietorship Firm
Depending upon the type and turnover of the proprietorship firm, following are the compliances involved:

How to get your Sole Proprietorship Firm compliance done from TaxHelpdesk?
Once your order is placed, one of tax experts from TaxHelpdesk will be assigned for you. The expert will get in touch with you within 24 working hours to understand your requirements. If there will be any requirements of documents from your end, then the same shall be intimated by the TaxHelpdesk expert. The documents can be uploaded by you in your designated account.
Details of Compliances of Sole Proprietorship Firm
1. Income Tax Return
The sole proprietorships are required to file annual income tax return during each financial year, unless they are exempted. Further, the income rate applicable on this sole proprietorship firm is same as that of a proprietor.
The Income Tax Return can be filed either physically or online via e-filing portal of Income Tax. The sole proprietorship firms can file their income tax return through form ITR-3 or ITR-4.
ITR-3 Form:
ITR-3 Form is to be filed by the proprietor having Income under the head ‘Profits or Gains of Business or Profession’.
ITR-4 Form:
ITR-4 or SUGAM form is applicable for sole proprietorship firm having total income up to ₹50 lakh and having Income from Business and Profession which is computed on a presumptive basis.
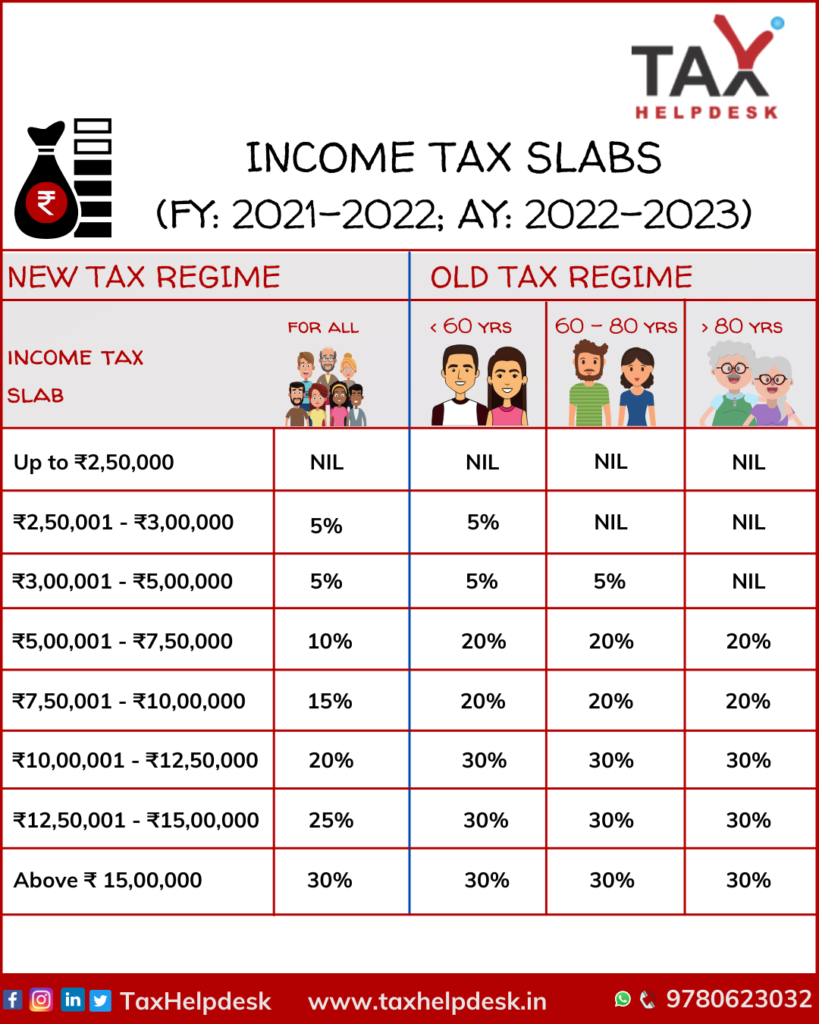
Income Tax Slab Rate
As stated above, the sole proprietor and sole proprietorship firm are same in the eyes of the law. Therefore, the Income Tax rate applicable for the firm will be same as that of a proprietor.
Note:
– The rates of Surcharge, Marginal Relief and SHE Cess are same under both the tax regimes and shall be levied/provided, where applicable.
– Rebate under Section 87-A of the Income Tax Act for resident individual whose total income is not more than ₹5,00,000 is also eligible for a rebate of 100% of Income Tax or ₹12,500, whichever us less. This rebate is also available under both the tax regimes.
2.TDS Return Filing
The TDS Return is to be filed where the proprietor has a valid TAN and the type of return to be filed depends upon the purpose of deduction. The types of TDS Return are:
Form 24Q – TDS on Salary
Form 27Q – TDS where deductee is a non-resident, foreign company
Form 26QB – TDS on payment for transfer of immovable property
Form 26Q – TDS in any other case.
3. GST Return filing
The proprietor needs to get his sole proprietorship registered for GST, if the aggregate business turnover exceeds Rs. 20 lacs. As per the GST Act, the GST Returns are to be filed if the taxpayer is registered under GST.
The returns to be filed for Sole Proprietorship firm registered under GST are GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B. These returns contain the details of outward and inward supplies of taxable goods and services, payment of taxes and are to be filed monthly or quarterly, as per the scheme availed by the proprietor.
4.EPF Return filing
The proprietor is required to get EPF registration if it employs more than 20 persons and accordingly, filing of EPF Return becomes mandatory.
5.Accounting and bookkeeping
The sole proprietor is required to maintain books of account, if the sale/turnover/gross receipts from the business is more than Rs. 25,00,000 or the income from business is more than Rs. 2,50,000 in any of the 3 preceding years.
6.Tax Audit
Sole proprietor is required to have a tax audit carried out if the sales, turnover or gross receipts of business exceed Rs. 1 crore in the financial year. However, he may be required to get their accounts audited in certain other circumstances.
Note:
The threshold limit of Rs. 1 crore for tax audit is proposed to be increased to Rs. 5 crore w.e.f., AY 2020-2021, if the proprietor’s cash receipts are limited to 5% of the gross receipts or turnover. The Finance Bill, 2021 has proposed to further increase this limit from ₹5 crore to ₹10 crore for taxpayers who are having digital transactions.
List of documents required for compliance of Sole Proprietorship
Following are the documents required for compliance of sole proprietorship:
– PAN Card
– Aadhaar Card
– GST number, if applicable
– Details of sales and purchases
– MSME registration, if applicable
– Bank statements
– Credit card statements, if any
FAQs
Late filing or non filing of Income Tax Return on or before the due date, will attract a penalty of Rs. 200 per day.
Only a practising chartered accountant can conduct audit of proprietorship firm.
Income tax returns of the proprietorship firms can be filed online or offline. In case, the returns are filed offline, then the proprietor should print two copies of ITR-V and a copy of ITR-V has to be signed by the proprietor and be sent by ordinary post to Post Bag No. 1, Electronic City Office, Bengaluru–560100 (Karnataka) and the another copy is to be kept for his personal records.
Late filing or non filing of GST Return on or before the due date, will attract a penalty of Rs. 200 per day.



















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.