All About ITR online filing
Income Tax Return or ITR is a form through which the persons provide information about the income earned by them. Accordingly, the tax applicable is shown and paid by them to the Income Tax Department. Therefore, each person should know about ITR online filing and file Income Tax Return before or on the due dates of ITR filing in India. Additionally, filing of ITR prevents you from fine and penalties, too.
Various category of ITR Online Filing Taxpayer
The category of the taxpayer depends upon the type of income that he earns. Therefore, the taxpayer can fall into any of the following categories:
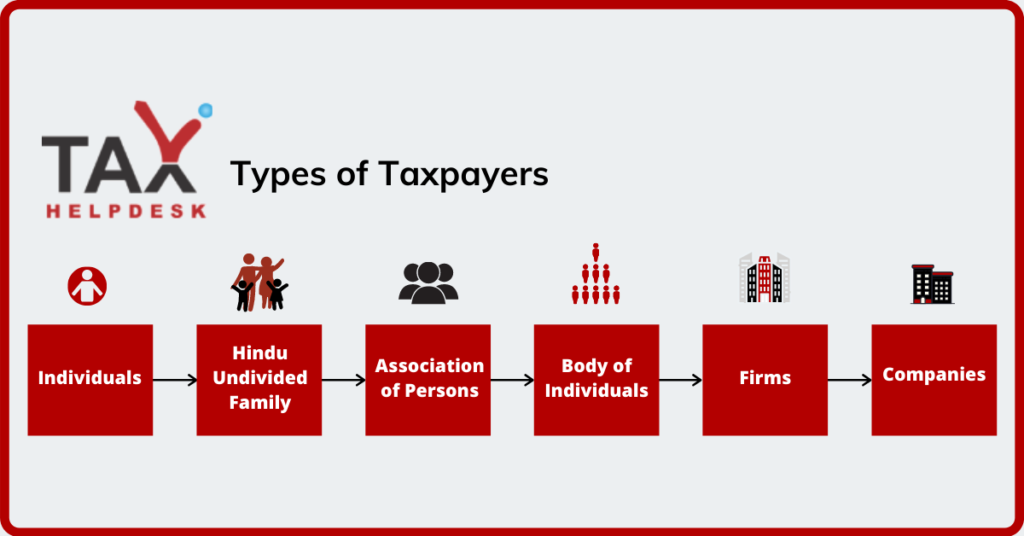
Who is required to do ITR online Filing?
The taxpayers have to file Income Tax Returns mandatorily if any of the following conditions are applicable to them:
Firstly, if the gross annual income of the taxpayer is above the following basic exemption limit:
| AGE GROUP | OLD TAX REGIME | NEW TAX REGIME |
|---|---|---|
| Individuals below 60 years | ₹2,50,000 | ₹3,00,000 |
| Individuals of age 60 years and above but below 80 years | ₹3,00,000 | ₹3,00,000 |
| Individuals above 80 years | ₹5,00,000 | ₹3,00,000 |
Note:
For the FY 2022-23, the threshold limit under the New Tax Regime is Rs. 2.5 lacs.
Secondly, if the taxpayer has more than one source of income like income from house property, capital gains, etc.
Thirdly, if the taxpayer either has earnings or investments in foreign assets during the relevant Financial Year
Lastly, if the taxpayer is a company or firm, irrespective of its profits or losses.
Which ITR should I file?
There are 7 different ITR forms through which an assessee can file his Return. Consequently, the assessee has to choose the correct ITR form for filing his ITR according to his source of income. Therefore, the following image illustrates the type of ITR form as per the source of income:
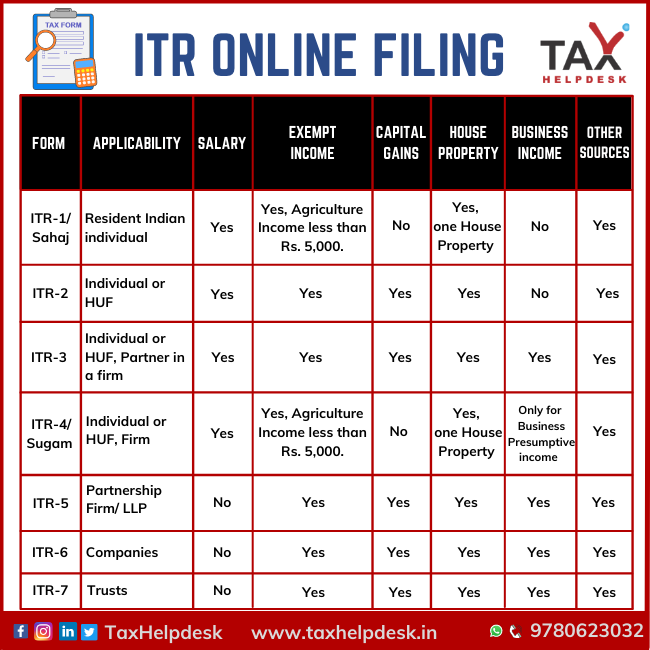
SAHAJ or ITR-1
SAHAJ or ITR-1 form applies to Resident Indian Individuals as well as HUFs having income from following sources:
- Pension or salary
- Agricultural income of not more than Rs.5,000
- Single house property income. However, in case the losses have been brought forward from the previous year, the exclusion is allowed.
- Other sources such as winning horse races, lottery, etc.
- Lastly, the maximum total income is Rs. 50 lakh.
Who cannot opt for ITR-1?
Either individuals or HUFs who fall under the following categories cannot opt for ITR-1:
- Total income that is more than Rs.50 lacs.
- Individuals have taxable capital gains.
- The income is from more than one house property.
- Investments in unlisted equity shares.
- Individual is either a Non-Resident Indian (NRI) or Resident Not Ordinary Resident (RNOR). That is to say, he is not a resident Indian.
- Individual is the director of a company.
- If there is income from property outside India.
- Lastly, the individual has foreign assets or foreign income.
ITR-2
The individuals and HUFs can use the ITR-2 form if they have income from following sources:
- Income is from pension or salary
- Income of the individual is more than Rs. 50 lakh.
- Agricultural income of the individual is more than Rs .5,000.
- Capital gains income
- House property income
- Income is from other sources like winning a lottery or horse races.
- The individual is the Director of a company.
- Lastly, investments are present in equity shares that were unlisted during the financial year.
Who cannot opt for this ITR-2?
Individuals who make an income either from business or profession cannot opt for the form ITR-2.
ITR 3
Individuals and HUFs having income from a profession or a proprietorship business have to file ITR through the ITR-3 form. In addition to this, the person may have income from following sources:
- In case any investments were present in equity shares that were unlisted at any time during the financial year.
- The individual is either a partner in a firm or director of a company.
- Additionally, income is from a pension or salary, house property, or any other source of income.
SUGAM or ITR 4
HUFs, Partnership Firms, as well as individuals who are Indian residents generating income from a profession or business must opt for ITR-4. However, Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs) cannot opt for this form.
In addition, individuals who have opt for the presumptive income scheme according to Section 44AD, Section 44ADA, and Section 44AE of the Income Tax Act 1961, should also opt for this form.
Who cannot use ITR-4?
Following individuals and HUFs cannot opt for ITR-4:
- Income is more than Rs.50 lakh.
- In case any losses have been brought forward from previous years.
- Individual has a signing authority at a place outside India.
- Investments are present in equity shares that are unlisted at any time during the financial year.
- The individual is a Director of a company.
- Furthermore, the individual is a non-resident or an RNOR. That is to say, if he is not a resident Indian.
ITR-5
Following persons have to file ITR-5:
– Firstly, investment funds,
– Secondly, business trusts,
– Thirdly, insolvent/deceased estate,
– Fourthly, Artificial Juridical Person,
– Fifthly, Body of Individuals, Associations of Persons,
– Lastly, LLPs and firms
Form ITR-6
Companies that are not claiming exemptions under Section 11 have to file income tax returns through the ITR-6. Furthermore, companies that can do ITR online filing under this section can only do it electronically.
ITR 7
Individuals as well as companies furnishing returns either under Section 139(4A), Section 139(4B), Section 139(4C), Section 139(4D), Section 139(4E), or Section 139(4F) must opt for this form. Moreover, given below are the details of the returns that must be filed under each section:
- Individuals who receive an income from a property that belongs to a trust or other legal obligations and the income whose generation is solely used for religious or charitable purposes. [Section 139(4A)]
- Political party, if the total income generation is more than the maximum amount. [Section 139(4B)]
- Filing of Returns must be filed under this section by the below-mentioned entities:
– Scientific Research association
– Institutions or associations that come under Section 10(23A)
– Medical institutions, hospitals, universities, funds, and other educational institutions, etc - College/university that do not require to furnish any income or loss [Section 139(4E)]
- Business/trusts that do not require to furnish any income or loss [Section 139(4E)]
- Lastly, investment funds [Section 139(4F)]
How to get your Income Tax Return Filed from TaxHelpdesk?
If you are searching the services related to the ITR filing near me? You are at the right platform after placing your order, TaxHelpdesk’s team for reviewing of documents will check your documents within 24 working hours. Thereafter, there will be an assignment of a Tax Expert. Accordingly, the processing of your order will take place. In addition to this, you also will be able to check the status of the order in your account.
FAQs
There are four ways of filing an Income Tax Return, which is as follows:
– Firstly, by furnishing the return in a paper form;
– Secondly, by furnishing the return electronically under digital signature;
– And lastly, by transmitting the data in the return electronically and thereafter submitting the verification of the return in Return Form ITR-V.
Filing of Income-tax return is mandatory for every person whose income (before considering certain exemptions and deductions) exceed maximum exemption limit.
In addition to this, the CBDT vide notification No. 37/2022, dated 21-04-2022, has notified additional conditions under the seventh proviso to section 139(1) whereby return filing is made mandatory. These conditions are as follows:
| Particulars | Amount |
|---|---|
| Individual has spent an aggregate amount exceeding for himself or any other person for foreign travel | Rs 2 lacs |
| Individual has deposited an amount or aggregate in one or more current accounts | Rs. 1 crore |
| Person has made deposits in a savings account | Rs. 50 lacs |
| Business turnover exceeds in a financial year | Rs. 60 lacs |
| Professional receipts is or more than in a financial year | Rs. 10 lacs |
| Total TDS/TCS amount deducted or collected is or more than | Rs. 25,000 |
| Individual has paid electricity bill on aggregate basis during the financial year | Rs 1 lakh |



















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.